Random Test Control Parameters
August 18, 2022
Back to: Random Testing
In a closed-loop vibration testing system, the controller outputs a signal through an amplifier to the shaker. A transducer then sends the response of the device under test (DUT) back to the controller. The system uses feedback to monitor and adjust the output based on the parameters set by the test engineer.
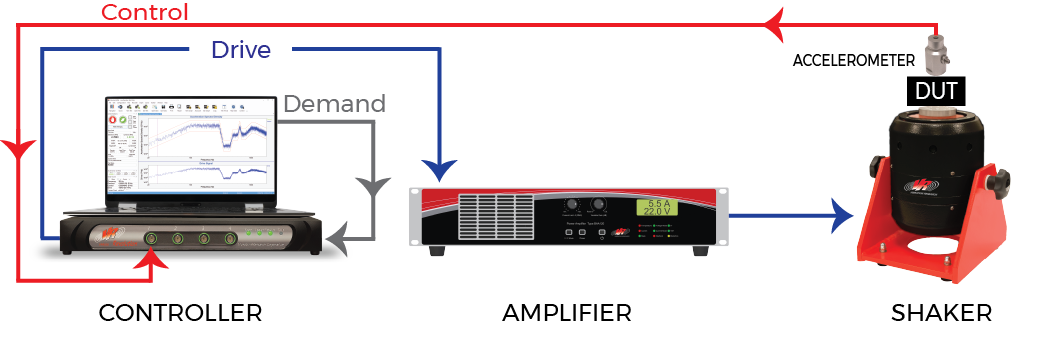
A control loop refers to the physical system and control functions that make adjustments to achieve the desired output. Adjusting these parameters determines how the control algorithm responds to the DUT’s response.
Random Test Control Parameters
In the VibrationVIEW Random test mode, the test engineer can define the control loop parameters on the Parameters tab in the Random Test Settings dialog box. In the context of this course, there are several parameters of note.
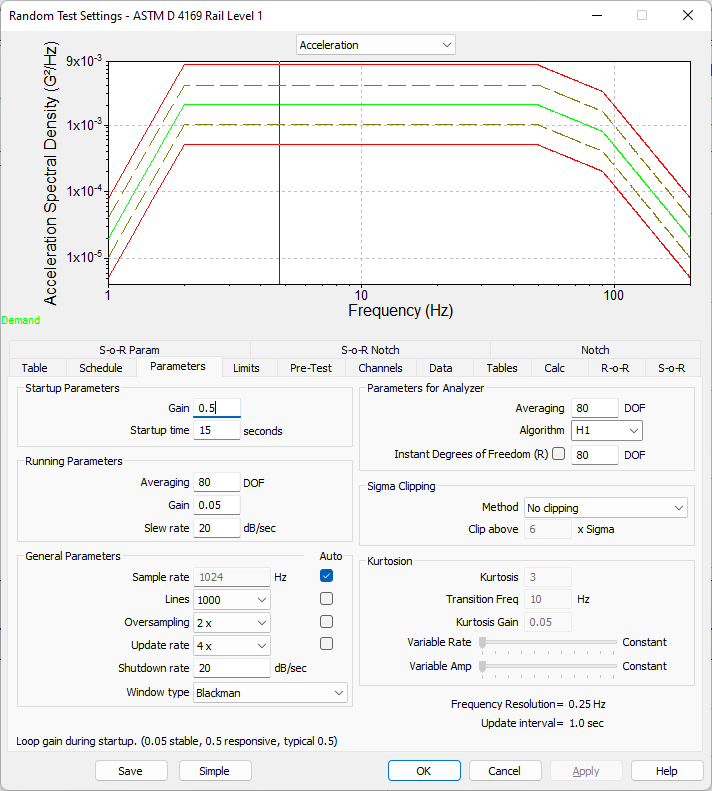
Random Test Settings dialog box in VibrationVIEW.
Averaging
The averaging degrees-of-freedom (DOF) parameter defines the statistical DOF factor the software uses to average the frequency data. The DOF value determines the number of independent pieces of information that the software incorporates into the frequency data.
The higher the DOF, the smoother the line, but the slower the controller will be to display changes. The time required to acquire a data block is determined by the block length, update rate, and sample rate.
Lines of Resolution
The Lines parameter defines the frequency resolution of the control loop. Increasing the number of lines allows for better control of low frequencies and sharp resonances, but the controller starts and responds slower to changing system dynamics.
An effective Lines value requires an appropriate sample rate and update rate. For example, to achieve 104,000 lines of resolution, set the sampling rate to 54,000, 60,000, or 65,536 or use 26,214.4 Hz at a 2x update rate.
Window Type
The Window type parameter configures the window type for the FFT computation. Windowing removes emphasis on discontinuities and reduces the leakage effects, as discussed in the Windowing lesson.
Sigma Clipping
The Sigma Clipping Method drop-down list includes different methods of limiting peak values in a random waveform. For Gaussian random data, the typical peak value is around 3 times the RMS. Less frequently, the waveform will contain peak values of 4 times the RMS and, rarely, it may exceed 5 times the RMS. The longer a random test runs, the more likely higher peaks become.
The Sigma Clipping Method allows the user to place an upper limit on the values produced by the controller. Clipping peaks will result in distortion; however, it can be a reasonable trade-off to limit the maximum peak values.
Read: When Should I Clip a Random Vibration Signal?
Random Vibration Testing Software
The VibrationVIEW Random test mode provides up to 104,000 lines of control with an easy-to-use interface. Users can analyze random data with a comprehensive suite of graph display options or generate a test from recorded data with our advanced test development options.
The following resource will take you through how to create a random vibration test in the VibrationVIEW software.
Video (42:05)
Fundamentals of VibrationVIEW Part 3 Random Vibration Testing
Download the free demo of VibrationVIEW today to set up and design tests before running them on a shaker, view and playback data files, and more. Interested in learning more? Visit the software page.
