Alternating and Direct Current
October 19, 2021
Fundamentals
Waveform Display
Domains for Analysis
Random Vibration
Back to: Introduction to Vibration Signals
Alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) help to define an electrical current.
In a DC, the electric charge always flows in one direction but may vary in voltage or current. As it only moves one way, a DC is either positive or negative and can be steady, smooth, or varied. Batteries, fuel cells, and solar cells all produce DC.
AC changes the direction of the current flow continuously. An AC changes from the positive to the negative in the shape of a sine wave. The rate of change in frequency is measured in hertz. Electric power from a wall socket is an AC. Most AC power supply alternates at 50 or 60Hz.
Signals in Vibration Testing
The signals analyzed in vibration testing are electrical signals generated by a flow of current and changing voltage. Conditioning is applied to the AC signal to perform a voltage (mV) to acceleration (G) conversion.
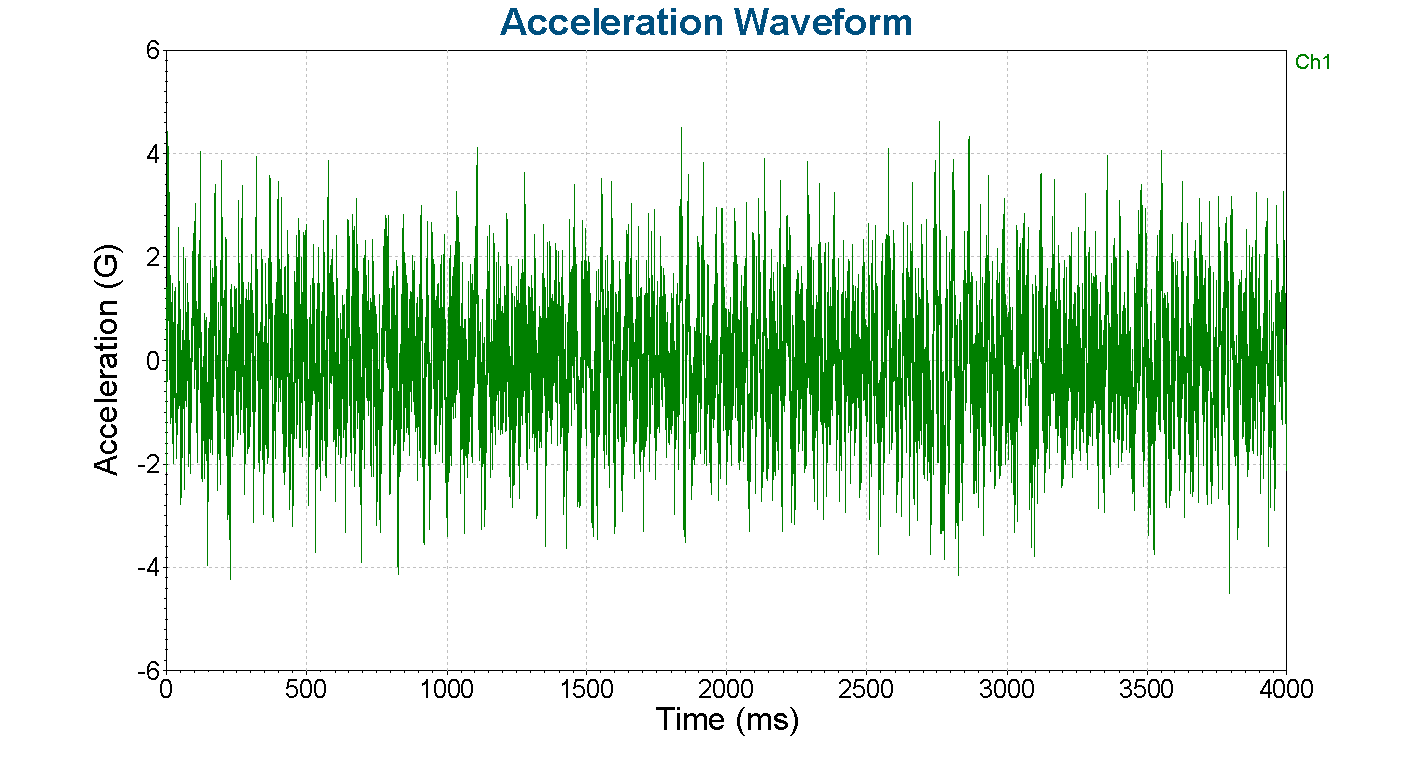
A simple random test acceleration waveform.
A graph of a constant signal reveals various properties, including amplitude, frequency, RMS values, and more. These properties are used to perform signal analysis and are the basis of vibration testing.
